The low differential pressure transmitter is a type of instrumentation equipment commonly used in modern industrial production, which can be called the “eye” of modern industrial production. In the production process, it can observe and control the pressure, flow, temperature, liquid level, and other measurement data of the entire production process. And then the data can be transferred to the logic algorithm in the central control system (DCS or PLC) through low DP data exchange. At the same time, adjustment is made by the regulator or control unit. Finally, the control of the production target values is completed. Thus, the low differential pressure transmitter is an important prerequisite for the establishment of a good control loop. Pressure transmitters and differential pressure transmitters are typical representatives of the “eye”, which are widely used due to their high precision and stability.
1. The classification of the low differential pressure transmitter
The function of the low differential pressure transmitter, in simple terms, is to convert the displacement or force of the elastic load cell into a standard electrical signal. Based on the composition and working principle, it can be divided into force-balance transmitter and displacement transmitter while the latter is generally used in the glass production line. Based on the measurement accuracy and objective, it can be divided into the micro differential pressure transmitter, the differential pressure transmitter, and the pressure transmitter. And besides, according to the signal transmission and power supply mode, it can be divided into a two-wire transmitter and a four-wire transmitter.
2. The application of the low differential pressure transmitter
Based on what we have learned, it is realized that the displacement transmitter is more approved by the market than the force-balance transmitter in today’s measurement field. The same is true in the design process of the glass production line. However, in terms of differences in measurement objectives and accuracy, there are still differences in the selection of the low differential pressure transmitter.
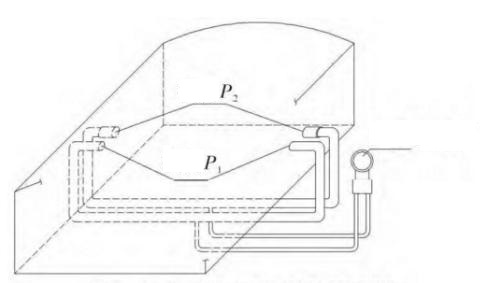
(1) The high-precision micro-differential pressure transmitter is used in the furnace to measure the pressure of the kiln, which is one of the fundamental safety and measurement objects. At this moment, the pressure pipe of P1 needs to go deep inside the furnace wall while the pressure of P2 is the atmospheric pressure at the temperature close to that of the furnace. The pressure pipe that is finally connected to the low differential pressure transmitter should be the average value of the pressure on both sides of the furnace. Next, based on the principle of the transmitter, the gauge pressure inside the furnace can be obtained through P1-P2.
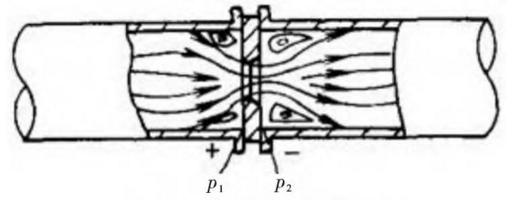
(2) The low differential pressure transmitter and the orifice plate flowmeters throttling device can be used for the measurement of natural gas, hydrogen, oxygen, and combustion-supporting airflow. A disk with a central hole is inserted into the pipeline. When the fluid passes through the orifice plate, the cross-section of the flow beam is reduced, causing a local difference in flow velocity and a relatively significant pressure difference. The flow rate of the fluid is proportional to the square root of the pressure difference before and after the throttle element under certain conditions. In the formula, Q is the measured flow, F0 is the opening area of the orifice plate, α is the flow coefficient, ρ is the liquid density, P1 is the inlet pressure of the orifice plate and P2 is the outlet pressure of the orifice plate.
In addition to its important role in the key measurement areas in the glass production line, the low differential pressure transmitter has many derivative applications, such as the measurement of the height change of the glass liquid level and the liquid level height, etc, which will not be described in detail here.
3. The development of the low differential pressure transmitter
Compared with liquid, it is more complicated to measure gas flow due to its compressibility. The volumetric flow rate Q of the gas is a function of the differential pressure (P1-P2) and the density ρ while the density is a function of the current temperature and pressure of the gas. In the practical application, there will be a large measurement error due to the difference between the current density of the medium and the density during design. Therefore, temperature and pressure compensation should be performed on it.
In the past, designers install both thermal resistance and a pressure transmitter near the location where the gas pipeline is set up the flowmeter. All three groups of signals are entered into the DCS system, and the compensation calculation is completed with the formula in the computer system. However, this model is gradually being replaced nowadays. With the emergence of a new generation of multi-parameter intelligent transmitters, this type of transmitter comprehensively improves the accuracy, reliability, and long-term stability of the low differential pressure transmitter by using a microprocessor as a basis.